
From Quantity to Quality: A Closer Look at Lifespan and Healthspan
Summary
Exploring the intricate relationship between lifespan and healthspan, this article delves into how our longevity is defined not just by the years we live but by the quality of life in those years.
- Distinction Between Lifespan and Healthspan: Highlights the difference between lifespan (total years lived) and healthspan (years lived in good health), emphasising the importance of quality life in the context of increasing global life expectancies.
- Challenges of Extended Lifespan: Discusses the medical advancements leading to longer lifespans but points out the gap between lifespan and healthspan, underlining the rise of chronic diseases in later life.
- Addressing the Healthspan Gap: Suggests the need for a holistic approach to health, incorporating preventive healthcare, lifestyle changes, and mental well-being to enhance the quality of life in aging populations.
Understanding the difference between lifespan and healthspan is crucial in longevity. Lifespan refers to the total number of years a person lives, encompassing the entire duration of an individual's life from birth to death. On the other hand, healthspan focuses more on the quality of those years, emphasising the time one spends in good health, free from chronic diseases and debilitating conditions. This distinction is becoming increasingly important as we see a global trend where people live longer. Still, unfortunately, a significant portion of their later years is spent grappling with poor health.
The Lifespan - Healthspan Gap
Increasing Life Expectancy
Advancements in medical science have led to a remarkable increase in global life expectancy. People live longer thanks to improved healthcare, nutrition, and living conditions. However, this triumph of increased lifespan brings with it new challenges.
Enhanced Healthcare Saves Lives
The remarkable progress in medical science over recent decades has significantly increased global life expectancy. This increase is a testament to many factors, including groundbreaking advancements in medical treatments, enhanced healthcare services, improved nutrition, and overall better living conditions. According to the World Health Organisation, global life expectancy at birth in 2016 was 72 years, up from around 66 years in 2000. This marked increase reflects a triumph in medical and health sciences and societal and environmental improvements.
We're All Living Into Our 80's
In many developed countries, the average life expectancy is even higher. For instance, in countries like Japan and Switzerland, average life expectancies have surpassed 83 years. This is a dramatic increase compared to a century ago when the average global life expectancy was below 50 years. The United Kingdom has also seen significant growth in this regard, with average life expectancy reaching into the late 70s and early 80s.
New Challenges
However, this success story of increased lifespan also introduces new challenges. Ensuring that these added years are spent in good health becomes more critical as people live longer. The rising number of elderly individuals in populations worldwide presents both economic and healthcare challenges, such as the need for long-term care and the increasing costs associated with treating chronic diseases, which are more prevalent in older age groups.
The Increasing Lifespan - Healthspan Gap
Furthermore, the disparity between lifespan and healthspan — the length of time people live in good health — is becoming increasingly evident. This gap highlights the importance of not just focusing on extending life but also on enhancing the quality of life as we age. As such, the focus of healthcare and social support systems is gradually shifting from merely increasing lifespan to improving healthspan, ensuring that the years gained are lived in good health and well-being.
The Burden of Ill Health in Later Years
The global increase in life expectancy has not been uniformly accompanied by an extension of healthspan, leading to a significant burden of ill health in later years. As people live longer, they are increasingly spending a substantial portion of their last years grappling with poor health, primarily due to chronic diseases. Conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, and other long-term ailments have become more prevalent, profoundly impacting the quality of life for many.
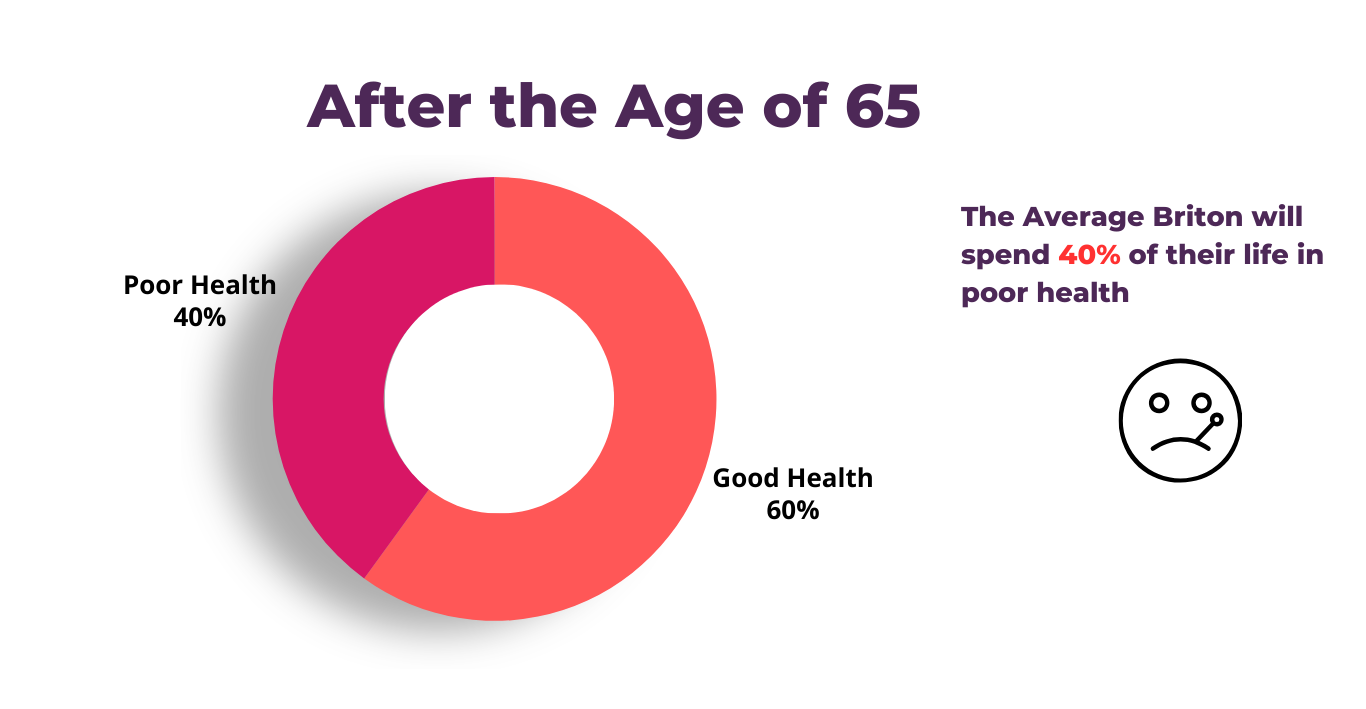
A Concerning Picture
Statistically, the situation presents a concerning picture. A study published in The Lancet found that, on average, men and women spend around 9 to 11 years in poor health. A large part of this ill health occurs in old age; at 60, it is estimated that over 40% of the remaining years will be spent in poor health. Another report by the World Health Organization revealed that individuals aged 60 and above typically live with some form of chronic condition for about the last eight years of their lives. These chronic conditions not only diminish the quality of life but also place a significant strain on healthcare systems.
Avoid the Four Horsemen

To live a long and healthy life you should try and avoid the so-called four horsemen of chronic disease: smoking, obesity, high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes.
In the context of chronic diseases, heart disease remains one of the leading causes of mortality and morbidity globally. The Global Burden of Disease Study indicates that cardiovascular diseases account for a significant proportion of years lived with disability among older adults. Diabetes, too, poses a significant health burden, with the International Diabetes Federation estimating that one in five people over the age of 65 live with diabetes.
Arthritis, another common condition affecting the elderly, contributes to reduced mobility and chronic pain, severely impacting their ability to lead an active and independent life. According to Arthritis Research UK, over 10 million people in the UK alone live with arthritis, highlighting the scale of this issue.
When a Longer Life Doesn't Always Mean a Better Life
This trend of extended lifespan not equating to a longer healthspan is particularly evident in developed countries, where healthcare systems are increasingly challenged to manage the growing needs of an ageing population. The discrepancy between living longer and living healthier raises essential questions about the effectiveness of current health interventions and the need for more focused strategies to treat and prevent these chronic conditions.
Extending Healthspan
The increasing years spent in chronic ill health underscore the need for a shift in focus from merely extending lifespan to enhancing healthspan. This requires a comprehensive approach involving public health initiatives, lifestyle modifications, and healthcare interventions that collectively aim to reduce the burden of chronic diseases and improve the quality of life in the elderly population.
A Global Issue
This phenomenon is not confined to any single region but is observed worldwide. The pattern of longer life but increased morbidity in old age is a common challenge from developed countries to emerging economies. For instance, research indicates that while life expectancy has increased globally, the years spent in good health have not kept pace, leading to extended periods of illness and dependency.
Learning from Diverse Health Models
Studying diverse health models worldwide offers invaluable insights into achieving longevity and well-being. For example, the Mediterranean diet, widely acknowledged for its heart health benefits and role in promoting longevity, emphasises a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, olive oil, and fish. This nutritional model is linked to reduced risks of chronic diseases and is celebrated for its balance and sustainability. It demonstrates the profound impact of diet on health and longevity.
The Importance of Emotional Well-being
On the other hand, the Japanese concept of 'Ikigai', which means finding a purpose in life, exemplifies the importance of mental and emotional well-being in living a long and fulfilling life. In regions like Okinawa, known for its high number of centenarians, Ikigai contributes to a lifestyle that intertwines personal satisfaction with community well-being. Such cultural practices underscore the significance of a holistic approach to health, integrating the physical, mental, and emotional aspects.
Diverse Approaches Work Best
These diverse approaches worldwide provide a rich tapestry of practices contributing to a healthier, longer life. They emphasise the importance of a balanced diet, mental well-being, and a purposeful life. By incorporating these varied practices into our lifestyles, we can create a more comprehensive and practical approach to health and longevity.
Personal responsibility
Enhancing healthspan undoubtedly requires a commitment to personal responsibility. It's about taking charge of your health through regular health check-ups, embracing an active lifestyle, and paying attention to mental and emotional well-being. These proactive steps are crucial in extending not just the length of life but the quality of those years. However, keeping up to date with the latest health best practices can be a daunting task. The ever-evolving landscape of medical research, dietary guidelines, and exercise regimens means that what is considered beneficial today might be revised tomorrow.
Stay Informed
This is where this website can be an invaluable resource. Understanding that staying informed is critical to making the best health decisions, we aim to simplify this process. It provides up-to-date, reliable information on health and wellness tailored to help individuals make informed decisions about their health. By offering insights into the latest research and emerging trends in nutrition, exercise, and mental health strategies, this website helps you navigate the complex world of health best practices.
A Higher Quality of Life
This support empowers you to take individual responsibility for your health in the most informed and effective way possible, ensuring that you live longer and enjoy a higher quality of life in those years. Remaing in good health and free from chronic illness.
